After the read, you will learn about the Cat M1 vs NB-IoT what are the differences.
What is NB-IoT?
Narrowband Internet of Things (NB-IoT), also known as LTE Cat NB1, is also a low-power wide-area (LPWA) technology, which has been developed to connect various devices to the Internet using existing mobile networks.
Narrowband Internet of Things (NB-IoT) has been developed to support the realization of the Internet of Things (IoT) applications. It is a low-power, narrow-band technology that can handle a small amount of two-way data transmission in an efficient, safe, and reliable way.
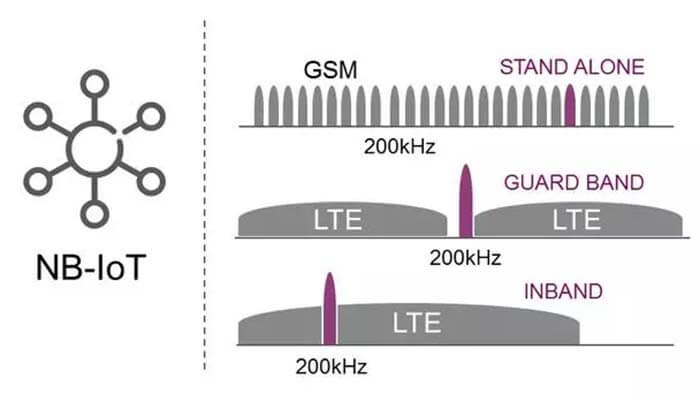
Figure 1 Deployment of NB-IoT
Narrowband Internet of Things (NB-IoT) technology uses the existing LTE network or spectrum resource blocks in the LTE carrier guard band to operate. It can also use the 200 kHz bandwidth spectrum that was previously used by GSM but is not currently used.
The NB-IoT specification was frozen in the 13th release of the 3GPP protocol specification (LTE-Advanced Pro) (namely 3GPP Release 13) in June 2016. According to the definition of Release 13, the technical specifications of NB-IoT are as follows.
Downlink peak rate: 250 kbps
Uplink peak rate: 250 kbps (multi-tone) and 20 kbps (single-tone)
Delay time: 1.6 to 10 seconds
Duplex technology: half-duplex
The device receiving bandwidth: 180 kHz
Equipment transmission power: 20/23 dBm
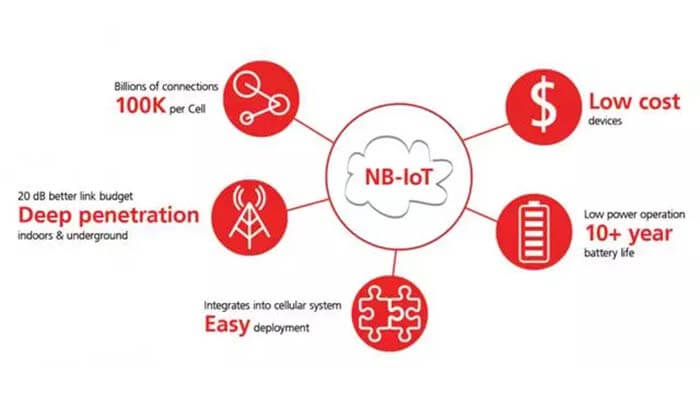
Figure 2 Key technical characteristics of NB-IoT
NB-IoT is one of the more popular LPWA technologies that can be used in Internet of Things (IoT) applications.
It provides the right combination of functions. The low-frequency narrowband signal on demand has long-distance propagation characteristics that can penetrate walls and metal conduits. The power requirements are low enough so that the life of a device powered by a single battery can exceed 10 years.
Its data rate is just right for Internet of Things (IoT) applications, such as meter readings, controlling street lights, parking space monitoring, industrial data monitoring, and some other low data rate applications.
What is LTE Cat M1?
LTE Cat M1 is a new low-power wide-area (LPWA) cellular technology specially designed for Internet of Things (IoT) and machine-to-machine (M2M) communications. It has been developed to support low to medium data rate applications with upload/download data rates below 1Mbps and can be used in half-duplex or full-duplex mode.
What are the Cat M1 VS NB-IoT differences?
LTE CAT M1 uses the existing LTE network for operation, but unlike NB-IoT, LTE CAT M1 operates in the same LTE frequency band used in cellular applications.
One of its advantages is that it has the ability to switch from one cell site to another, which makes it possible to use the technology in mobile applications;
However, NB-IoT does not allow mobile handover from one cell site to another cell site, so it can only be used for fixed applications, that is, applications limited to the area covered by a single cell site.
Because LTE Cat M1 technology can coexist with 2G, 3G, and 4G mobile networks, it has all the advantages of mobile network security and privacy features, such as supporting user identity confidentiality, entity authentication, confidentiality, data integrity, and mobile devices The function of identification, etc.
The latest LTE CAT M1 specification was approved in June 2016 in the version 13 agreement (3GPP Release 13) of the 3GPP specification (LTE-Advanced Pro). According to the definition of Release 13, the technical specifications of LTE CAT M1 are as follows.
Deployment: LTE frequency band in-band
Downlink peak data rate: 1 Mbps
Uplink (uplink) peak data rate: 1 Mbps
Delay time: 10-15 ms
Technical bandwidth: 1.08MHz
Duplex technology: full-duplex or half-duplex
Transmit power level: 20/23 dBm
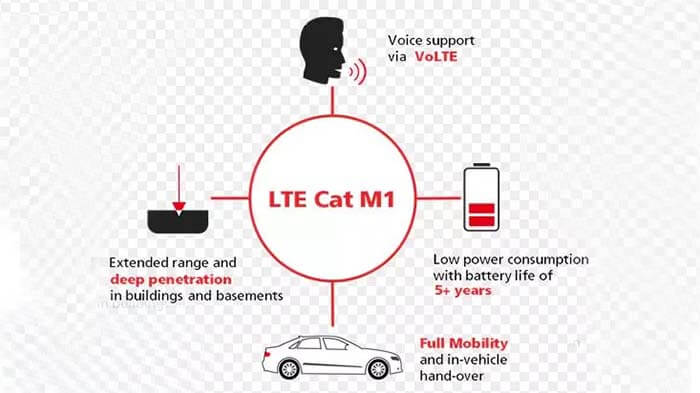
Figure 3 Key features of LTE Cat M1
The commercial network release of LTE CAT M1 is expected to take place this year or in 2017.
Based on the definition of 3GPP Release 13, the following table compares the key specifications of LTE Cat M1 VS NB-IoT.
| LTE Cat M1 | NB-IoT |
Deployment | In-Band LTE | In-Band LTE, LTE Guard Bands, Standalone |
Downlink Modulation | OFDMA, 16 QAM | OFDMA |
Downlink Datarate | Up to 1 Mbps | 250 kbps |
Uplink Modulation | SC-FDMA, 16 QAM | SC-FDMA |
Uplink Datarate | Up to 1 Mbps | 250 kbps (multi-tone), |
Bandwidth | 1.08 MHz | 18o khz |
Duplexing Technology | Full Duplex, Half Duplex,FDD & TDD | Half Duplex and FDD |
Lateney | 10 to 15 milli seconds | 1.6 to 10 seconds |
Link Budget | 155.7 dB | 164 dB |
Power Class | 23 dBm, 20 dBm | 23 dBm, 20 dBm |
Table 1 Comparison of key specifications between NB-IoT and LTE CAT-M1
You may also be interested in the below articles.
Internal Antenna VS. External Antenna
LTE Vs. 5G: Is 5G Better Than LTE?



