
About WiFi 6 Mean For The Enterprise
About WiFi 6 Wi-Fi 6 introduces some new technologies to help mitigate the issues that come with putting dozens of Wi-Fi devices on a single network. It lets
C&T RF Antennas Inc provides wireless antennas and wireless solutions for various network environments…

The Internet of Things is an important part of a new generation of information technology. Simply put, it is the Internet that connects everything.
The Internet of Things is the Internet of things connected. This has two meanings.
First, the core and foundation of the Internet of Things is still the Internet, which is an extension and expansion network based on the Internet;
Second, its user end extends and extends to any item and item, for information exchange and communication.
The definition of the Internet of Things is to use radio frequency identification (RFID), infrared sensors, global positioning systems, laser scanners, and other information sensing devices to connect any item to the Internet according to an agreed agreement for information exchange. And communication to realize the intelligent identification, positioning, tracking, monitoring, and management of items.
The Internet of Things is regarded as the application extension of the Internet. Application innovation is the core of the development of the Internet of Things, and innovation with user experience as the core is the soul of the development of the Internet of Things.
The Internet of Things is a network based on information carriers such as the Internet and traditional telecommunications networks, allowing all ordinary physical objects that can be independently addressed to achieve interconnection. It has three important characteristics: ordinary object equipment, autonomous terminal interconnection, and pervasive service intelligence.
The Internet of Things refers to the ubiquitous end devices and facilities, including sensors with inherent intelligence, mobile terminals, industrial systems, building control systems, home smart facilities, Video surveillance system, etc. and externally enabled.
For example, various assets affixed with RFID, intelligent objects such as individuals and vehicles carrying wireless terminals or animals or intelligent dust (Mote) are interconnected through various wireless/wired long-distance/short-distance communication networks ( M2M), Grand Integration, and SaaS operations based on cloud computing.
Provide safe, controllable, and even personalized real-time online monitoring, positioning traceability, alarm linkage, dispatch command, plan management, remote control, security prevention, remote maintenance, online upgrades, statistical reports, decision support, leadership desktop (Cockpit for centralized display Dashboard) and other management and service functions to realize the integration of management, control, and operation of all things with high efficiency, energy-saving, safety, and environmental protection.
The Internet of Things is a dynamic global network infrastructure. It has self-organization capabilities based on standards and interoperable communication protocols. Physical and virtual things have an identity, physical attributes, virtual characteristics, and intelligent interfaces, and are connected to information Seamless network integration. The Internet of Things will form the Internet of the future together with the Internet of Media, the Internet of Services, and the Internet of Enterprises.
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the real-time collection of any information sensors, radio frequency identification technology, global positioning system, infrared sensors, laser scanners, and other devices and technologies that need to be monitored, connected, and interacted The object or process of the collection of various required information such as sound, light, heat, electricity, mechanics, chemistry, biology, location, etc.,
Through various possible network access, to realize the ubiquitous connection of objects and objects, objects and people, to realize the intelligent perception, recognition, and management of objects and processes. The Internet of Things is an information carrier based on the Internet and traditional telecommunications networks. It allows all ordinary physical objects that can be independently addressed to form an interconnected network.
Compared with the traditional Internet, the Internet of Things has its own distinctive features.
First of all, it is a wide application of various perception technologies.
A large number of sensors of various types are deployed on the Internet of Things, and each sensor is an information source, and the information content and information format captured by different types of sensors are different. The data obtained by the sensor is of real-time nature, collecting environmental information periodically at a certain frequency, and constantly updating the data.
Second, it is a ubiquitous network built on the Internet.
The important foundation and core of the Internet of Things technology is still the Internet. Through the integration of various wired and wireless networks with the Internet, information about objects can be accurately transmitted in real-time.
The information collected by sensors on the Internet of Things needs to be transmitted through the network. Because of its huge amount, it forms a huge amount of information. In the transmission process, in order to ensure the correctness and timeliness of the data, it must be adapted to various heterogeneous networks and protocols.
Thirdly, the Internet of Things not only provides the connection of sensors, but it also has the ability of intelligent processing, which can implement intelligent control of objects.
The Internet of Things combines sensors and intelligent processing and uses various intelligent technologies such as cloud computing and pattern recognition to expand its application areas. Analyze, process, and process meaningful data from the massive information obtained by the sensors to adapt to the different needs of different users and discover new application fields and application modes.
The things here must meet the following conditions to be included in the scope of the Internet of Things:
There must be a data transmission path;
Must have a certain storage function;
Need a CPU;
Need an operating system;
There must be a dedicated application;
Follow the communication protocol of the Internet of Things;
There is a unique number that can be identified in the world network.
Private IoT: generally provides services to a single organization;
Public IoT: Provide services to the public or large user groups based on the Internet;
Community IoT: Provide services to an associated community or group of organizations (such as various commissions and bureaus under a city government, such as the Public Security Bureau, Transportation Bureau, Environmental Protection Bureau, Urban Management Bureau, etc.);
Hybrid IoT: It is a combination of two or more of the above-mentioned Internet of Things, but there is a unified operation and maintenance entity in the background.
Smart homes have made great progress in the past two years. Experts believe that sales of Amazon’s smart device Echos during the 2016 holiday season have been more than 9 times higher than the previous year. Smart home technology will become more important after 2018. According to the Smart Home Technology Survey, 70% of consumers who have already purchased smart home devices are highly likely to buy again.
In 2015, sales of wearable devices reached 78.1 million pieces; by 2020, the market has grown to 411 million pieces. All wearable technologies, including smartwatches, fitness trackers, and VR devices, have generated a lot of data, and companies have only just begun to understand the possibilities and potential application value contained in them.
By 2021, 82% of cars will be connected to the Internet. The emergence of the Internet of Things has changed the automotive industry and has produced application integration, navigation, diagnostic tools, in-car entertainment, and even autonomous vehicles. At the same time, the huge investment that the automotive industry is going through will determine the next innovation content of the Internet of Things.
In the manufacturing industry, the transformation and upgrading of the manufacturing industry around the world around Industry 4.0, Industrial Internet, and intelligent manufacturing has been set off.
The deployment of industrial robots in particular has become the direction of many large-scale manufacturing industries. The use of machines to replace dangerous, simple, and repetitive tasks has been widely used. Quoted in major production bases around the world.
The Internet of Things technology has created a new era of smart cities, from smart cameras to the deployment of various sensors to collect various data in the city, and after processing by cloud AI technology, it will help improve traffic and streets and other cities. Public management capabilities.
More and more cities around the world are actively embracing the Internet of Things in order to enhance the city’s refined management capabilities. The main features include: smart citizens, smart transportation, smart economy, smart environment, smart life, smart government, based on digital city, with GIS + sensors + ICT + wifi as the backbone, 5G, AI, AV and government, enterprises and the masses Association is everywhere and everywhere.
Intelligent shipping is a new form of modern shipping formed by the deep integration of traditional shipping elements with modern information, communications, sensing, and artificial intelligence. It includes five aspects, smart ships, smart ports, smart shipping, smart shipping services, and smart shipping supervision.
RFID is a simple wireless system consisting of an interrogator (or reader) and many transponders (or tags). The tags are composed of coupling elements and chips. Each tag has an electronic code with only one extended entry, which is attached to the object to identify the target object.
It transmits radio frequency information to the reader through the antenna, and the reader is the device to read the information.
RFID technology allows items to “speak”. This gives the Internet of Things a feature that can be traceable. That is to say, people can grasp the exact location of the object and its surrounding environment at any time.
MEMS is the abbreviation of Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems. It is an integrated microdevice system composed of microsensors, microactuators, signal processing and control circuits, communication interfaces, and power supplies.
The goal of MEMS is to integrate the acquisition, processing, and execution of information to form a multi-functional micro-system and integrate it into a large-scale system, thereby greatly improving the automation, intelligence, and reliability of the system. It is a more versatile sensor.
Because MEMS has given ordinary objects new life, they have their own data transmission channels, storage functions, operating systems, and specialized applications, thus forming a huge sensor network. This allows the Internet of Things to monitor and protect people through objects.
M2M is the abbreviation of Machine-to-Machine/Man, which is a networked application and service centered on the intelligent interaction of machine terminals. It will enable the object to achieve intelligent control.
M2M technology involves five important technical parts: machines, M2M hardware, communication networks, middleware, and applications. Based on the cloud computing platform and intelligent network, it is possible to make decisions based on the data obtained by the sensor network and change the behavior of the object for control and feedback.
Cloud computing aims to integrate multiple relatively low-cost computing entities into a perfect system with powerful computing capabilities through the network and use advanced business models to allow end-users to obtain services with these powerful computing capabilities.
In the next ten years, it is estimated that there will be about 25 billion network-connected devices, which is more than the number of personal computers, mobile phones, and tablet computers combined. This is a very large connection.
The Internet of Things is a huge network of connected objects. This relationship is between people, people, and things, things and things. Therefore, one of the biggest factors affecting the Internet of Things is data, the amount of data, and the management and use of data.
IIoT stands for Industrial Internet of Things, IIoT also called industry IoT.
The industrial internet of things (IIoT) refers to the extension and use of the internet of things (IoT) in industrial sectors and applications.
Industrial Internet of Things is the continuous integration of various acquisition and control sensors or controllers with perception and monitoring capabilities, as well as mobile communications, intelligent analysis, and other technologies into all aspects of the industrial production process, thereby greatly improving manufacturing efficiency, improving product quality, and reducing products cost and resource consumption will eventually achieve a new stage of upgrading traditional industries to intelligence.
In terms of application form, the application of the Industrial Internet of Things has the characteristics of real-time, automation, embedded (software), security, and information interoperability.
IIoT is essentially machine-to-machine (M2M) support extended to the cloud.
Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is the use of radio frequency identification technology, sensors, two-dimensional codes, and other technologies to obtain information and data at all stages of the product from the production process to sales to end-users.
The traditional industrial automation system information collection only exists in the production quality inspection stage, and the enterprise information system does not pay much attention to the specific production process.
The Industrial Internet of Things is a way to connect a dedicated network to the Internet to transmit equipment information accurately and accurately in real-time. It is extremely dependent on the network and pays more attention to data interaction than traditional industrial automation information systems.
Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is the use of intelligent computing technologies such as cloud computing, cloud storage, fuzzy recognition, and neural networks to analyze and process data and information, combined with big data, to dig deeper into the value of data.
A fully functional industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) system should have the functions of self-organization and self-maintenance. Each node must provide the entire system with information and decision-making data obtained by its own processing. Once a node fails or the data is abnormal or changed, the entire system will automatically make corresponding adjustments based on the logical relationship. It must be interconnected in all directions.
The research of industrial Internet of Things technology (IIoT) is an interdisciplinary project, which involves the fields of automation, communication, computer, and management science. The wide application of the Industrial Internet of Things needs to solve many key technical problems.
Inexpensive sensors with good performance are the cornerstones of industrial Internet of Things applications. The development of the industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) requires more accurate, smarter, more efficient, and more compatible sensor technologies.
Intelligent data collection technology is a new direction in the development of sensor technology. The ubiquity of information puts forward higher requirements on industrial sensors and sensing devices.
In most cases, companies will build the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) based on existing industrial systems. How to realize that the sensors used in the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) can be compatible with the sensors already used in the original equipment is one of the problems facing the promotion of the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT).
The compatibility of the sensor mainly refers to the compatibility of the data format and the compatibility of the communication protocol. The key to compatibility is the unification of the standards.
At present, protocols such as Profibus and Modbus commonly used in industrial Fieldbus networks have solved compatibility problems. Most industrial equipment manufacturers have developed various sensors and controllers based on these protocols.
The network is one of the cores of the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), and data is transmitted through the network between different levels of the system. The network is divided into wired networks and wireless networks. The wired network is generally used in the cluster server of the data processing center, the internal LAN of the factory, and some Fieldbus control networks, and can provide high-speed and high-bandwidth data transmission channels.
The industrial wireless sensor network is an emerging technology that uses wireless technology for sensor networking and data transmission. The application of wireless network technology can greatly reduce the wiring cost of industrial sensors, which is conducive to the expansion of sensor functions.
Industrial information has exploded. The large amount of data generated in the process of industrial production is a challenge for the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT).
How to effectively process, analyze, and record these data, and extract the results of guiding recommendations for industrial production, is an industrial thing. The core of networking is also the difficulty.
Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) security mainly involves data collection security, network transmission security, and other processes. Information security plays a key role in enterprise operations.
For example, data collection in metallurgy, coal, petroleum, and other industries requires a long-term continuous operation. How to ensure that data collection And the accuracy of the information in the transmission process is a prerequisite for the application of the Industrial Internet of Things to actual production.
Enterprises can use the Internet of Things (IoT) technology to timely grasp raw material procurement, inventory, sales, and other information. Through big data analysis, they can also predict the price trend of raw materials, supply and demand relations, etc., which will help improve and optimize the supply chain management system and improve the efficiency of the supply chain. reduce costs.
The ubiquitous perception characteristics of the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) improve the ability and level of production line process detection, real-time parameter collection, and material consumption monitoring. Through the analysis and processing of data, smart monitoring, smart control, smart diagnosis, smart decision-making, and smart maintenance can be realized. Productivity, reduce energy consumption.
The use of sensor technology to monitor the health of production equipment can track the use of various industrial machinery and equipment in the production process in time, and gather data through the network to the equipment manufacturer’s data analysis center for processing, which can effectively diagnose and predict machine faults. Quickly and accurately locate the cause of the failure, improve maintenance efficiency, and reduce maintenance costs.
The integration of industrial Internet of Things and environmental protection equipment can realize real-time monitoring of various pollution sources and key indicators of pollution control links generated in the industrial production process.
Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) technology can monitor the safety status information of operators, equipment, machinery, and surrounding environment in real-time by installing sensors in dangerous operating environments such as mining equipment, oil and gas pipelines, and mining equipment, and obtain all-around safety elements in the production environment.
To upgrade the existing network supervision platform to a systematic, open, and diversified comprehensive network supervision platform, effectively guaranteeing the safety of industrial production.
Industrial IoT solutions can provide real-time information on equipment performance and personnel to help simplify and improve business processes and work processes.
Using professional energy-saving management data to help companies better conduct R&D and production will help promote corporate innovation and improve production efficiency.
Companies can use the insights gained from IoT data to develop new products and services.
The industrial IoT platform can provide all identity management functions, such as secure authentication and authorization, to ensure that IoT endpoints are not subject to cyber-attacks.
Using the Internet + big data to drive intelligent operation and management, based on the collection of real-time operation data, combined with analysis, operation, instruction, management, and other functions, help companies make accurate and efficient energy-saving decisions and realize smart energy management systems.

AIoT (Artificial Intelligence Internet of Things) = AI (Artificial Intelligence) + IoT (Internet of Things).
AIoT integrates AI technology and IoT technology, generates and collects massive amounts of data through the Internet of Things, and stores them in the cloud and at the edge. Then, through big data analysis, and higher forms of artificial intelligence, it realizes the digitization of everything, the intelligent connection of everything, and the Internet of Things technology pursuit of artificial intelligence is an intelligent ecosystem.
In addition to the need for continuous innovation in technology, the implementation and application of technology is the core issue that needs to be broken through in the field of Internet of Things and artificial intelligence at this stage.
AIoT is not a new technology, but a new form of IoT. Therefore, some people think that AIoT is a combination of artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) in practical applications, and a transition from the Internet of Everything to the Intelligent Connection of Everything.
The full name of AloT is Artificial Intelligence & Internet of Things, which is a broad sense refers to the integration of artificial intelligence technology and the Internet of Things in practical applications, but with the arrival of the 5G wave, the connotation of AloT has become more abundant.
AIoT is not a simple AI+IoT but applies artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things, and other technologies, based on big data, cloud computing, semiconductors as algorithm carriers, network security technologies as implementation guarantees, and 5G as a catalyst for data, Knowledge, and intelligence.
Emerging technologies such as 5G and AI will explode in 2019, bringing more and more application scenarios such as autonomous driving, urban brains, AI elderly care, and medical imaging into our lives.
With the characteristics of high speed, large capacity, and low latency, 5G brings more efficient information transmission channels to the Internet of Things (IoT). It is used in smart homes, car networking, unmanned driving, smart cities, smart medical, and smart Rural areas and other fields that have broad prospects.
The blessing of AI technology provides a smarter information collection portal and richer application scenarios for IoT. AI can pull a relatively isolated device into the scene, which can greatly improve the response space of IoT.

About WiFi 6 Wi-Fi 6 introduces some new technologies to help mitigate the issues that come with putting dozens of Wi-Fi devices on a single network. It lets
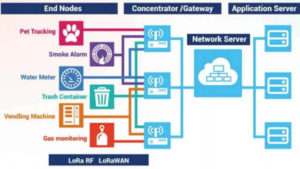
In this article, we will analyze the most common standards for IoT applications, Various wireless technology solutions in the IoT, Bluetooth low energy (blue), Wi-Fi, and
The Bluetooth personnel location tracking management system is a location-based personnel management system. The system adopts technologically advanced Bluetooth positioning technology, wireless communication technology, and computer
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |
WhatsApp us