What is the radio frequency of RFID transmission characteristics? What is the advantage of RFID technology?
The most important advantages of the RFID system are non-contact recognition, which can wear through snow, fog, ice, coatings, dust, and barcodes that cannot be used in harsh environments, and the reading speed is extremely fast, and in most cases less than 100 milliseconds.
After more than 20 years of effort, ultra-high frequency RFID technology has become one of the core technologies of the Internet of Things, and the annual shipments have reached 20 billion levels.
In this process, China has gradually become the main production country of ultra-high frequency RFID label products, and under the strong support of the development of the Internet of Things, the IoT industry application and the whole ecology have been very rapid.
Here are 5 RFID transmission characteristics of radiofrequency
Attenuation in RFID transmission characteristics
It is not possible to avoid attenuating in RF propagation, from a literal understanding, attenuation is to reduce the strength of the RF signal.
Accurately, when the signal is propagating in RFID transmission medium, some energy is converted into thermal energy or is absorbed by the transfer medium, thereby causing signal strength to weaken, which is called attenuation. As shown, the signal of the ultra-high frequency RFID reader is decreased by the decrease in the decrease in the aqueous medium. General attenuation is represented by L (LOSS):
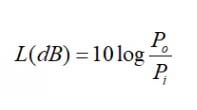
Where PO represents the attenuation of the power; PI indicates the power before attenuation. The DB of L in the case of attenuation is a negative value, and the PO is less than Pi.
The picture shows the signal attenuation in the RFID transmission schematic

Where are the places of the attenuation in RF transmission?
In the cable: the resistance between the cable and the joint causes RF to convert to thermal energy.
In the air: The energy spread caused by the path is the maximum factor of attenuation, dust, and rain in the air cause attenuation.
The passive device fever in the system causes the RF signal attenuation.
An attenuator (beneficial) added in the system is added.
It is very emphasized that attenuation is not necessarily a bad thing. Many times, in order to protect the circuit, attenuate at the front end of the circuit, or control the radiation range before the antenna output is decay, it is a matter of meaning against the entire system.
The gain in RFID transmission characteristics
RF gain in RFID transmission characteristics
The gain is a characteristic opposite attenuation, and the result is an increase in RF signal strength. Radio gain (non-antenna gain) is generated by active devices. It will be appreciated that enlarged energy is to be enlarged, and it is necessary to give it corresponding energy. General gain is represented by GAIN.
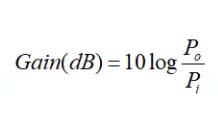
Where PO indicates the output power, the Pi represents the input power. In the case of attenuation, the DB of GAIN is a negative value, and the PO is less than Pi; the dB of GAIN is positive in the gain condition, and the PO is greater than Pi. If the positive gain is implemented, you need to introduce external energy and provide an amplifier to achieve signal amplification.
As shown in the figure above, it is a schematic diagram of attenuation and gain, where the signal is reduced by the amplitude after the passive device attenuates and generates heat loss; the amplitude is reinforced by the energy gain provided by the active device. One thing to note is that regardless of the gain or attenuation, the frequency of operation is consistent with the original.
Antenna gain in RFID transmission characteristics
The antenna gain needs to distinguish between the radio frequency gain, the gain of the antenna is completely different from the transmission gain of radiofrequency. The gain of the antenna is an increase in energy intensity in a particular direction rather than increasing its total energy.
The antenna is generally a passive device that cannot be provided with additional energy enhancement RF signals. As shown in Figure, a schematic diagram of a satellite microwave antenna, the emission, and reception of antenna is to bring all energy on the main wave, and there is no new energy increase.
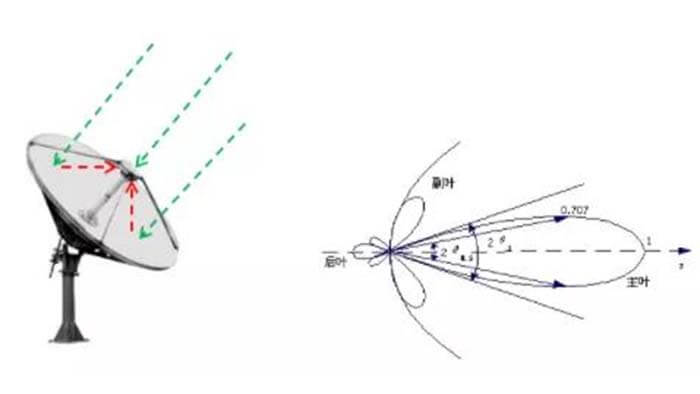
Satellite microwave antenna radiation schematic
Reflection in RFID transmission characteristics
Many objects cause reflections on the RF signal. When the incident wave encounters the reflection surface, the reflection is reflected, and the size of the reflection is related to the frequency of the RF signal and the material of the object.
Such as concrete has a certain reflection on the RF signal; the metal is almost completely reflected by the RF signal; the ionosphere is absorbed by long waves, but the short wave, the ultra short wave absorbs less and gets more reflection.
The direct result of the reflection is to cause multipath effects, and the receiving end will receive the same signal from different paths. Multipath signals can destroy or cancel the direct signal, causing cavities or blind spots in the signal coverage area, affecting communication quality.
This is the root source that affects the identification rate of RFID in warehouses and other applications.
Refraction in RFID transmission characteristics
Birefringence is a transmission direction deflection in the transmission direction that occurs when an RF signal passes through different densities. Such as cold air, the fog, that will cause RF to refract.
On the intersection of the two objects, RF also refers to the object in addition to reflection. When communicating the long-distance RFID transmission, the refractive block causes a serious problem. Such as when the atmospheric layer changes, RF will change the direction and deviate from the destination so that the communication cannot be performed.
Scattering in RFID transmission characteristics
Scattering is a reflected form, and the RF signal is scattered in a non-uniform reflector, referred to as scattering. Dust, fog, leaves, irregular rocks, etc. can cause scattering. Ultra-high frequency RFID tags are communications with the reader using reverse scattering techniques.
Besides the What Are The RFID Transmission Characteristics article, you may also be interested in the below articles.
Internal Antenna VS. External Antenna
LTE Vs. 5G: Is 5G Better Than LTE?



