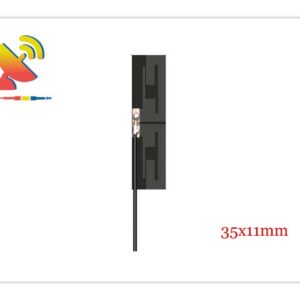
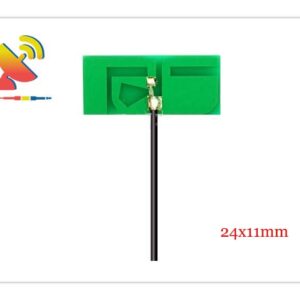
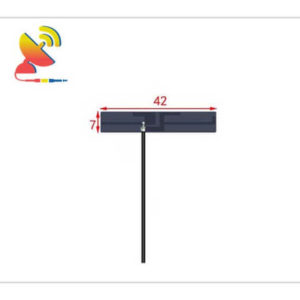
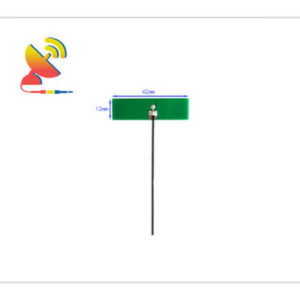
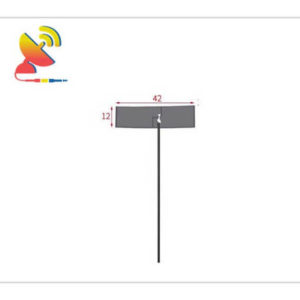
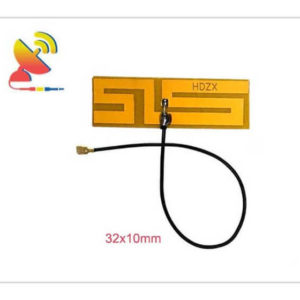
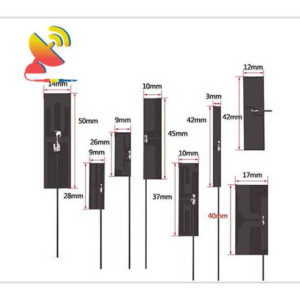
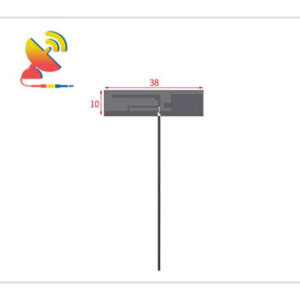
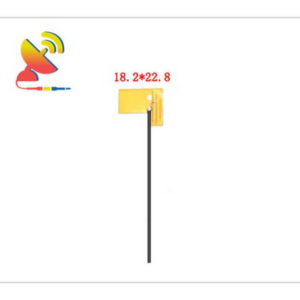
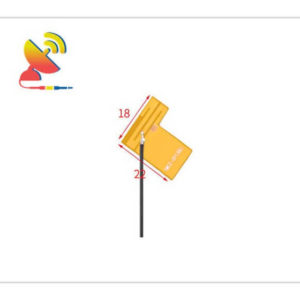
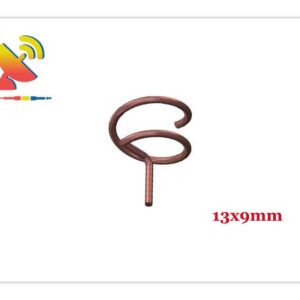
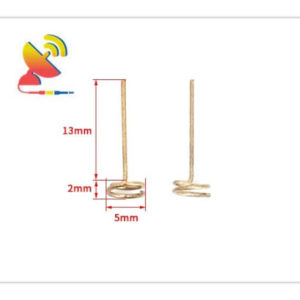
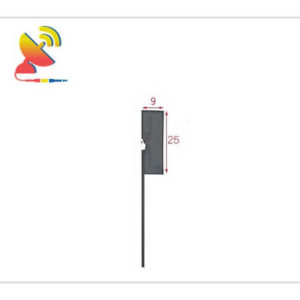
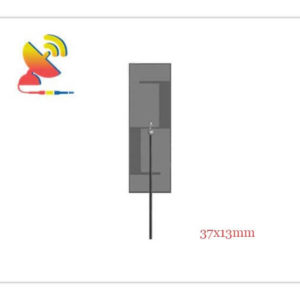
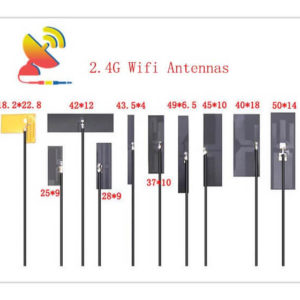
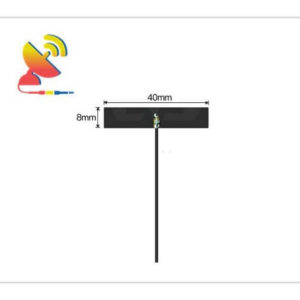
2.4 GHz Antenna
What is 2.4 GHz?
2.4 GHz wireless technology is a short-range wireless transmission technology for open source use. 2.4 GHz refers to a frequency band in which to operate.
2.4GHz ISM (Industry Science Medicine) is a wireless frequency band that is openly used worldwide, and Bluetooth technology works in this band. The technology is used for wireless transmission and conduction over short distances.
2.4 GHz advantages
Wide range of applications
It is a global operating band, and products developed for global versatility can use this band for a wide range of wireless products and is widely used in indoor applications such as personal wearable devices and wireless broadband routers.
High Bandwidth
Its overall bandwidth is better than other ISM bands, which increases the overall data transmission rate, allows system coexistence, allows bi-directional transmission, is highly resistant to interference, and has a long transmission distance (short-range wireless technology range).
Low power consumption
The antenna of the 2.4 GHz radio is quite small and the product size is smaller, resulting in a more focused chip and less power consumption. Due to the advantages of 2.4 GHz wireless technology, manufacturers are constantly introducing new technologies, which also makes this technology develop rapidly.
2.4 GHz technology standards
2.4 GHz ZigBee/IEEE 802.15.4
2.4 GHz ZigBee technology is an emerging short-range wireless communication technology, mainly for the application area of Low Rate Wireless Personal Area Network (LRWPAN).
Typically characterized by proximity, low power consumption, low cost, and low transmission rate, it is mainly used in the field of automation and remote control and is intended to meet the wireless networking and control of small and inexpensive devices.
The 2.4 GHz band is a global brand, while 868 MHz and 915 MHz are ISM bands used in the USA and Europe, which have been introduced to avoid interference from various wireless communication devices around 2.4 GHz.
At the same time, ZigBee also has some shortcomings such as small transmission range, low data transmission rate, and uncertainty of time delay.
2.4 GHz Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi (Wireless Fidelity), the IEEE 802.11 protocol, is a short-range wireless transmission technology that can support radio signals for Internet access within a range of several hundred feet.
The first version of WiFi was published in 1997, which defined the Media Access Control Layer (MAC layer) and the Physical Layer. The basic network architecture and basic transmission medium of a wireless LAN were specified, and the characteristics of the physical and medium access layers (MAC) were standardized.
The physical layer uses infrared, DSSS (direct sequence spread spectrum), or FSSS (frequency modulation spread spectrum) technology. 1999 saw the addition of the IEEE 802.11a and IEEE 802.11g standards. Its transmission rate can reach up to 54 Mb/s and can support a wide range of services such as data, image, voice, and multimedia.
Wi-Fi, or Wireless Local Area Network, operates in the 2.4 GHz band and is used in schools, businesses, and other office areas for wireless connectivity at transmission rates of up to 54 Mbit/s and operating distances of up to 100 m using Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS).
The main driver for the adoption of Wi-Fi is data throughput, and Wi-Fi is generally used to connect computers and wireless devices to a local LAN or directly to the Internet.
Because Wi-Fi uses radiofrequency technology to send and receive data through the air, it uses radio waves to transmit data signals and is more susceptible to outside interference.
Data packets can be detected or received by the outside world during transmission, making information security a concern. Although data can be encrypted and transmitted, there is still the possibility of hacking if there are enough packets.
2.4 GHz Bluetooth
The Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG) has announced the official adoption of Bluetooth specification version 4.0 and the launch of the corresponding certification program.
In addition to the high-speed transmission technology added to the 3.0+ HS version of the standard, the 4.0 version adds the Wibree low-power transmission technology previously pushed by Nokia. This makes Bluetooth 4.0 a “triple play” combining IEEE 802.15.1 legacy Bluetooth, IEEE 802.11 physical and MAC layers, and the Wibree standard.
The low-power transmission part is the focus of Bluetooth 4.0 and follows the former Wibree standard. Using simple GFSK modulation, it has extremely low operating and standby power consumption and can operate for years on a single coin cell battery. There is no doubt that
The new low-power Bluetooth will challenge technologies such as ZigBee and NFC. The network topology of low-power Bluetooth is much simpler than the star topology of Zig-Bee and the transmission distance has a significant advantage over NFC.
Data transmission: Bluetooth low-power technology supports very short data packets with transmission speeds of up to 1 Mb/s. All connections use an advanced sniffing sub-rated function mode for ultra-low load cycles.
Latency: Bluetooth Low Power technology enables online establishment in as little as 3 ms, as well as the ability to quickly start the linker with an application and close the connection as soon as the approved data transfer is completed with milliseconds of transfer speed.
Stability: Bluetooth Low Power technology uses a 24-bit cyclic repeat check loop (CRC) to ensure maximum stability of all packets in the event of interference.
High security: AES-128 full encryption using CCM provides a high level of encryption and authentication for data packets.
The disadvantages of Bluetooth technology are undeniably as obvious as the advantages: the data transmission bottleneck. High-speed frequency hopping makes Bluetooth transmissions extremely secure but also limits the possibility of data packets being too large during Bluetooth transmission, even in the advertised high-fidelity Bluetooth headsets, which are heavily compressed in the high and low-frequency sections.
2.4 GHz Wireless USB
Wireless USB technology achieves a maximum transmission rate of 480Mbit/s at a distance of 3m while performing at the same level as the existing USB 2.0.
Wireless USB specifies a rate of 110Mbit/s for 10m and uses the globally available 2.4 GHz ISM band to communicate over distances of up to 10m and connect up to 8 devices.
Wireless USB is not a networking solution, so there is no associated cost or power overhead, and supports USB plug-and-play without the need for drivers and standards/certification processes.
2.4 GHz Disadvantages
In order to automate control in industry, homes, and buildings, freeing humans from wired environments with the goal of replacing wires, short-range wireless communication technology standards for the Wireless Personal Area Network (WPAN, Wireless Personal Area Network) range have been rapidly developed, with typical technology standards such as Bluetooth, ZigBee, Wireless USB, Wireless LAN Wi-Fi, etc.
While people are enjoying convenience and speed, the electromagnetic compatibility issues of these technologies are increasingly coming to the fore. As these technologies all choose the 2.4 GHz (2.4 to 2.483 GHz) ISM band, coupled with sources of interference such as cordless phones and microwave ovens, it makes the band increasingly crowded.
C&T RF Antennas Inc is the internal 2.4GHz Antenna and external 2.4GHz Antenna manufacturer in China, we supply 2.4 GHz antennas with many antenna types.
The 2.4GHz Wifi antenna types are including Through-hole Mount Antennas, Magnetic Mount Antennas, Rubber Duck Antennas, Fiberglass Antennas, PCB Antennas, FPC Antennas, Spring Antennas, etc.
C&T RF Antennas Inc provides RF antennas with Dualband wifi 2.4G, wifi 5.8G, 169 MHz, 230 MHz, 315 MHz, 433 MHz, 868 MHz, 915 MHz, UWB, RFID, ADS-B, ISM, GPS, GNSS, Cellular, Lora, NB-IoT, GSM, 4G LTE, 5G NR, 6G, etc. for the Wi-Fi And Bluetooth industries, IoT And M2M industries, LoRa And ISM applications, and GPS And GNSS applications.
Buying Guide for the Wi-Fi 2.4 GHz antenna
Gain: What are the dBi of the Wi-Fi 2.4 GHz antennas?
1dBi to 20dBi high gain antennas.
VSWR: What is the VSWR of the Wi-Fi 2.4 GHz antennas?
≤1.5 for single-band frequencies, ≤2.0 for dual-band frequencies, and ≤3.0 for multi-band frequencies.
Impedance: What is the impedance of the Wi-Fi 2.4 GHz antennas?
50 Ω.
Frequency: What are the frequencies of the Wi-Fi 2.4 GHz antennas?
The frequencies include 2400-2500 MHz.
Direction: What are the directions of the Wi-Fi 2.4 GHz antennas?
Omnidirectional & directional.
Polarization: What is the polarization of the Wi-Fi 2.4 GHz antennas?
Vertical polarization.
Price: How much do the Wi-Fi 2.4 GHz antennas cost?
Based on different Wi-Fi 2.4 GHz antenna models.
Antenna Type: What are the types of Wi-Fi 2.4 GHz antennas?
Dipole & Molopole antenna.
Cable Type: What are the cable types of Wi-Fi 2.4 GHz antennas?
RG Cable.
Connector: What are the connectors of the Wi-Fi 2.4 GHz antennas?
Ipex, u.FL, MHF, SMB, Fakra, SMA, BNC, TNC, N-type, etc.
Size: What are the sizes of the Wi-Fi 2.4 GHz antennas?
Different Wi-Fi 2.4 GHz antenna has different sizes.
Material: What are the materials of the Wi-Fi 2.4 GHz antennas?
Plastic, Glass fiber, Magnet, PCB, Copper coil, Flexible PCB, etc.
Weight: What are the weights of the Wi-Fi 2.4 GHz antennas?
Based on different Wi-Fi 2.4 GHz antenna models have different weights.
Color: What are the colors of the Wi-Fi 2.4 GHz antennas?
Grey, black, white, yellow, green.
Operation Temperature: What is the operating temperature of the Wi-Fi 2.4 GHz antennas?
-40˚C ~ +85˚C.
Storage Temperature: What is the storage temperature of the Wi-Fi 2.4 GHz antennas?
-40˚C ~ +80˚C.
Safety Emission: What is the safety emission of the Wi-Fi 2.4 GHz antennas?
RoHS/CE Compliant.
Features: What special features does the Wi-Fi 2.4 GHz antenna have?
Low-Profile, Low V.S.W.R, Low Loss, High Gain, High Efficiency, High Sensitivity, UV-Proof Water Proof, Sturdy, Durable, Good Impact Resistance, Full Day Working, Optimized Dimensions, etc
Mounting Method: What are the mounting methods of Wi-Fi 2.4 GHz antennas?
Screw-mounted, Terminal mount, Based mount, Pole mount, etc.
Application: What are the applications of Wi-Fi 2.4 GHz antennas?
ISM, Wifi, Bluetooth, Sigfox, Zigbee, Z-wave, IoT, M2M, etc.
Select C&T RF Antennas Inc’s 2.4 GHz antennas where maximum varies as well as dependability is essential. We have 2.4 GHz antennas for utilization both indoors as well as outdoors, making certain that you do not deal with constraints when preparation out a plan for your interaction systems.
Most of our 2.4 GHz antennas are portable, without compromising anything in regards to efficiency, as well as are suitable for scenarios where area goes to costs or the antenna calls for assimilation into a smaller sized room.
For any technical questions or any issues connected to our online sales, do not wait to get in touch with our C&T RF team.
Showing 1–16 of 163 results