What is LiDAR (laser radar)?
LiDAR combines radar-ranging capabilities with camera angular resolution and is used to provide accurate depth perception sensing to complete the image (Figure 1).
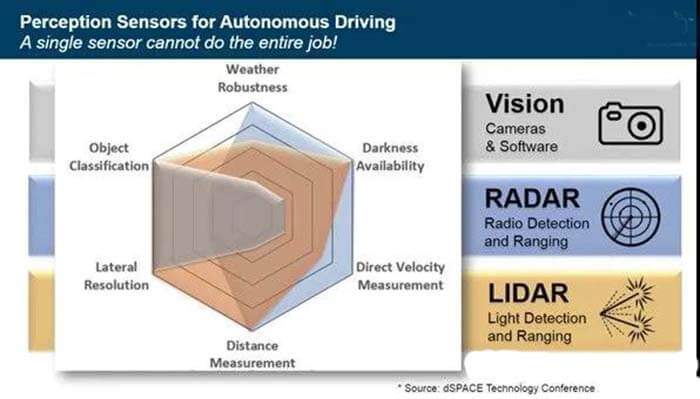
Figure 1: Cameras, radar, and LiDAR are the three preferred technologies for autonomous vehicle driving. (Image source: ADI)
The vision component represents the visibility, object classification, and lateral resolution of the camera or driver. Darkness and weather conditions such as snow, dust, or rain can diminish these capabilities.
The radar component represents the return of the RF signal. This signal is unaffected by weather conditions and darkness, while also measuring distance.
The LiDAR portion can complete the sensing picture by providing further object classification, lateral resolution, ranging, and darkness penetration.
How does LiDAR work?
The basic elements of a LiDAR system include a square wave transmitter system, a target environment, and an optical receiver system used to interpret the distance of external elements in the environment.
The lidar sensing method uses light in the form of a pulsed laser and measures range by analyzing the time of flight (ToF) of the returned signal (Figure 2).
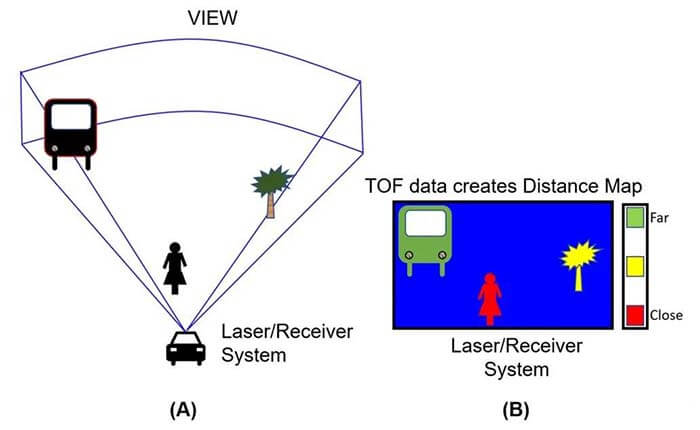
Figure 2: Each LIDAR transmitter unit has a triangular “field of view”. (Image source: Bonnie Baker)
The plotting of distance depends on the optical digital signal.
Signals in the digital domain
The circuit solution for LIDAR is to solve the signal reception problem by means of an automotive inter-trans-impedance amplifier. Its input stage is used to accept negative input current pulses from the photodetector (Figure 3).
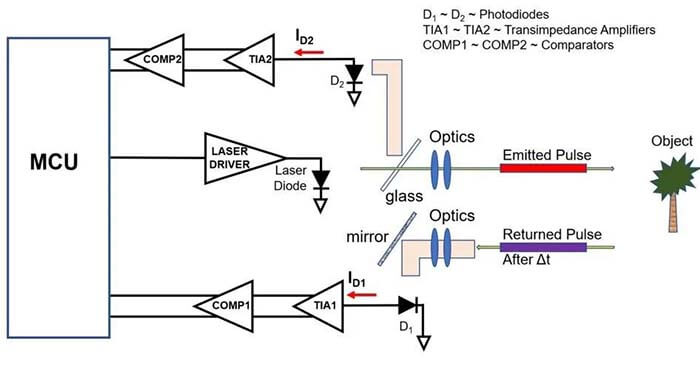
Figure 3: The electronic part of the LIDAR consists of a laser diode transmitter and two photodiode receivers. (Image source: Bonnie Baker)
The laser diodes are transmitting a digital pulse signal through a piece of glass. This signal is also reflected back to the D2 photodiode. The processing of this signal provides the transmission time and the electronic delay built into the system.
The digital light signal pulse is shot at the object and reflected back to the optical system. The returned pulse is mirrored to a second photodiode D1.
The electronic portion of the D1 signal path is the same as the D2 signal path. Both signals reach the microcontroller (MCU) and the time of flight can be calculated.
Market Snapshot
Automotive LiDAR systems use pulsed lasers to measure the distance between two vehicles. Automotive systems use LIDAR to control vehicle speed and braking systems to respond to sudden changes in traffic conditions.
LiDAR plays an important role in semi-autonomous or fully automated vehicle assistance functions such as collision warning and avoidance systems, lane-keeping assistance, lane departure warning, blind-spot monitors, and adaptive cruise control.
Automotive LiDAR is replacing the radar systems in earlier automotive automation systems. The range of LIDAR systems can range from a few meters to more than 1,000 meters.
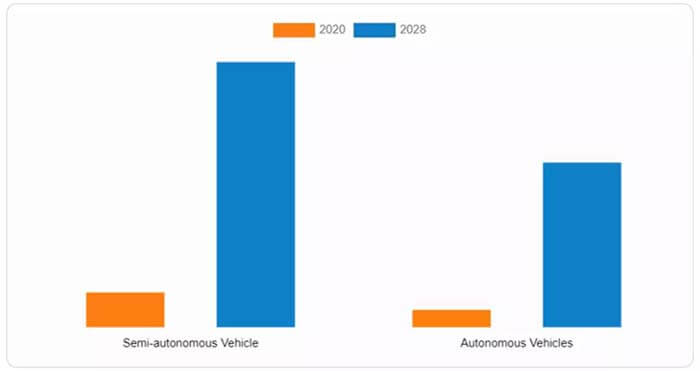
Figure 4: The automotive LiDAR market is segmented into semi-autonomous and fully autonomous vehicle applications. (Image source: Allied Market Research)
Self-driving cars are already widely used and lidar imaging systems will further improve the situation.
Radar, cameras, and LiDAR devices remain the technology of choice for semi-autonomous and fully autonomous driving today, and the price of LiDAR is falling as the market accelerates this change.
Besides the article, you may also be interested in the below articles.
What Is The Core 5G NR Technology?



