After the read, you will learn the characteristics of the 6 wireless protocols IEEE protocols: LoRa, NB-IoT, ZigBee, Wi-Fi, BLE, and WiMax.
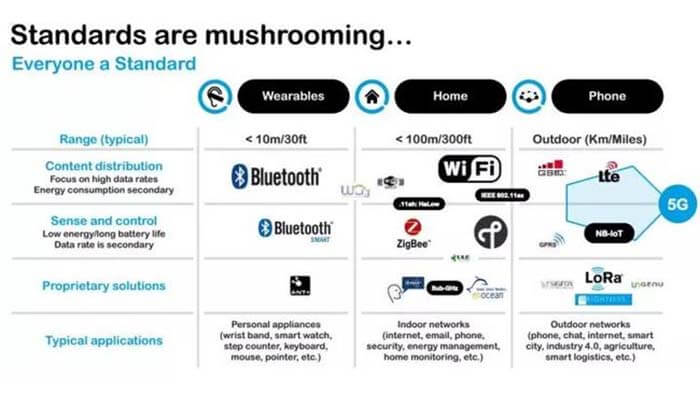
In the field of IoT, a wide range of communication technologies and wireless protocols exists simultaneously. In terms of transmission distance, there are BLE, WI-FI, ZigBee, sub1G, etc., which are widely used in the context of local wireless networks, such as wearable, home, and enterprise applications.
For wide-area wireless networks wireless protocols, there are LoRa, NB-IoT, eMTC, etc., which are specifically applied to low-rate, low-power, wide-coverage IoT services.
According to the latest data from market research firm Gartner, 72% of all IoT connections will use short-range transmission technologies wireless protocols like WIFI and ZigBee by 2025. And low-power, wide-area coverage networks that include technologies like Sigfox, LoRa, and NB-IoT will account for 11% of IoT connections in 2025.
There are many wireless communication technologies and wireless protocols for the IoT, which fall into two main categories.
One category of wireless protocols is short-range communication technologies such as Zigbee, WiFi, Bluetooth, and Z-wave.
The other category of wireless protocols is LPWAN (low-power Wide-Area Network), a wide-area communication technology.
LPWAN wireless protocols can be further divided into two categories.
One category of LPWAN wireless protocols is technologies such as LoRa and SigFox which operate in unlicensed spectrum.
The other category of LPWAN wireless protocols is 2G/3G/4G cellular communication technologies that work in licensed spectrum and is supported by 3GPP, such as EC-GSM, LTE Cat-m, NB-IoT, etc.
High-rate services mainly use 3G and 4G technologies; medium-rate services mainly use GPRS technologies.
Low-rate services do not yet have good cellular technology to meet them, while it has a rich and diverse range of application scenarios, which in many cases can only be supported reluctantly using GPRS technology.
Wireless protocols allow devices to establish a network connection and communicate with each other without the need for wired cables, and this article will detail the characteristics of each of the five wireless protocols IEEE protocols.
The various types of wireless networks support devices to communicate with each other or with the web (TCP/IP network) without the need for cables.
A variety of different wireless technologies and wireless protocols are currently being used in hardware products for the Internet of Things (IoT) and machine-to-machine (M2M) communications.
The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) has seven 802.15 Technical Task Groups. These IEEE organizations set standards for common types of wireless technology for personal local area networks.
These 802.15 task groups include WPAN/Bluetooth, Coexistence, High Rate WPAN, Low Rate WPAN, mesh networks, body area networks, and visible light communications.
Each IEEE wireless protocol has its own unique benefits and limitations. Continued investment in development has led to an increasing value and potential for the application of these wireless protocols.
LoRa wireless protocols

LoRa stands for Long Range and belongs to a group of wireless communication technologies typically characterized by long-range and low power consumption. The rate is relatively low and can be regarded as physical layer implementation in network communication. The corresponding product of LoRa is the transceiver chip, which mainly handles binary data streams.
LoRaWAN is a set of wireless protocol standards based on the MAC layer on top of LoRa physical layer transmission technology, corresponding to the data link layer (MAC layer) in the OSI seven-layer model. LoRaWAN eliminates the incompatibility of specific hardware and also realizes multi-channel access, frequency switching, adaptive rate, channel management, timing transceiver, node access authentication, data encryption, roaming, and other features.
The common LoRa modules on the market usually implement physical layer communication. To implement the LoRaWAN function, you need to use software to implement the LoRaWAN wireless protocols, and to implement the network communication function, you also need a gateway.
LoRa is one of the LPWAN communication technologies and is an ultra-long-range wireless transmission solution based on spread spectrum technology adopted and promoted by Semtech in the US.
This solution changes the previous compromise between transmission distance and power consumption, providing users with a simple system that enables long-range, long battery life, high capacity, and thus extended sensing networks. Currently, LoRa operates mainly in the global free frequency bands 169 MHz, 315 MHz, Asia 433 MHz, EU868 MHz, and US915 MHz.
LoRa technology has long-range, low power consumption (long battery life), multi-node, and low-cost characteristics.
NB-IoT wireless protocols

The Narrow Band Internet of Things (NB-IoT) is an important branch of the Internet of Everything.
Built on cellular networks, NB-IoT consumes only about 180 kHz of bandwidth and can be deployed directly on GSM, UMTS, or LTE networks to reduce deployment costs and enable smooth upgrades.
NB-IoT is an emerging technology in the IoT space that supports cellular data connectivity for low-power devices over wide area networks (LPWAN).
NB-IoT supports efficient connectivity for devices with long standby times and high network connectivity requirements. It is said that the battery life of NB-IoT devices can be increased to at least 10 years, while still providing very comprehensive coverage of indoor cellular data connections.
As a new standard technology, NB-IoT is under competitive pressure from Sigfox and LoRa technologies (more mature industry chain and earlier commercial adoption).
However, Sigfox and LoRa belong to unlicensed bands and are not favored by operators and equipment vendors.
Although the NB-IoT market is promising, there is also a price war behind the heat. The cost of NB-IoT is extremely low and will drop to US$1 with large-scale applications, while the cost of a single connection module is currently stuck at US$5.
The price of chips for Bluetooth, Thread, and ZigBee is around US$2, and the price of a chip supporting only one of these standards is less than US$1. This price gap makes enterprises think about NB-IoT when they have to consider the issue of cost advantage, and although operators are actively promoting it, there is still a long way to go before the technology is finally truly productized.
IEEE 802.15.4: ZigBee wireless protocols

LPWAN is the most rapidly growing organization in wireless technology today, and ZigBee is an open, global standard designed for M2M networks.
The technology offers low cost and low power consumption, making it an ideal solution for many industrial applications. The ZigBee wireless protocols provides 128-bit AES encryption.
In addition, the technology supports Mesh networks, allowing network nodes to be connected together over multiple paths.
The most common application scenario for ZigBee wireless protocols is in the area of smart home devices. The technology’s ability to connect multiple devices together at the same time makes it ideal for home networking environments, allowing users to communicate between devices such as smart locks, lights, robots, and thermostats.
The ZigBee Alliance has recently standardized this technology in the hope that connectivity will be more compatible and universal.
Currently, all ZigBee devices are unable to communicate directly with other ZigBee devices from different manufacturers. It is hoped that the development of standardization will rectify this problem and lead to these devices offering uniform functionality to end-users.
IEEE 802.11: Wi-Fi wireless protocols

WiFi uses radio waves (RF) to enable two devices to communicate with each other. The technology is commonly used to connect devices such as computers, tablets, and mobile phones to a router to access the Internet.
It can be used to connect virtually any two hardware devices. WiFi is a local wireless network developed by the IEEE running on the 802.11 standards.
WiFi protocols can use both the global 2.4GHz UHF ISM band and the 5GHz SHF ISM radio band.
The WiFi Alliance certifies some products and allows them to be marked as “Wi-Fi Certified”. In order to receive this designation, products must pass the Alliance’s interoperability certification tests.
802.11b, 802.11g, and 802.11n wireless protocols operate in the 2.4GHz ISM band. This band is susceptible to interference from some Bluetooth devices as well as some microwave ovens and mobile phones.
Devices operating on both of these bands can operate in the US without an FCC license but still require FCC Part 15 certification. The first six channels of each channel are considered to be part of the private radio band.
IEEE 802.15.1: Bluetooth and BLE wireless protocols

Bluetooth and Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) are wireless protocols technologies used for data transmission over short distances. The technology is often used for small devices that can be connected to the user’s mobile phone and tablet. For example, the technology is mostly used in various voice systems.
Low-power Bluetooth is less powerful than standard Bluetooth wireless protocols and is used in fitness trackers, smartwatches, or other small hardware that connects devices for wireless data transmission without a significant impact on the battery power in the user’s phone.
BLE has only recently started to be widely used. The technology was originally introduced by smartphone manufacturer Nokia in 2006 but did not become part of the Bluetooth standard until 2010.
Today, BLE is known as Smart Bluetooth and is supported by most smartphone and computer manufacturers, as well as most major operating systems including Windows 8, OS X, Linux, Windows Phone, Android, and iOS.
Bluetooth uses UHF radio waves for data transmission. The technology was originally standardized as IEEE 802.15.1, but today the IEEE no longer maintains that particular standard.
Companies that use Bluetooth are usually part of the Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG). The SIG currently has over 20,000 members and must certify products before they can be marketed as Bluetooth devices to consumers or businesses.
This certification helps to ensure that all Bluetooth devices work in a standardized way and provide similar product functionality to consumers.
IEEE 802.16: WiMax wireless protocols

WiMax stands for Worldwide Interoperable Microwave Access Technology. This wireless technology allows data to be transmitted at a rate of 30-40 megabits per second. The technology is specifically made interoperable by the IEEE 802.16 wireless family.
At one time several mobile operators (notably Sprint) used WiMax to deliver wireless data to their customers. However, Sprint and other operators using the technology have now switched to the faster LTE 4G network for data transmission.
The WiMax organization certifies devices before they are sold to consumers or businesses. The technology can be used both indoors and outdoors, but WiMax devices generally have better signals when used outdoors.
Besides the Characteristics of the 6 Wireless Protocols article, you may also be interested in the below articles.
What Is The Core 5G NR Technology?