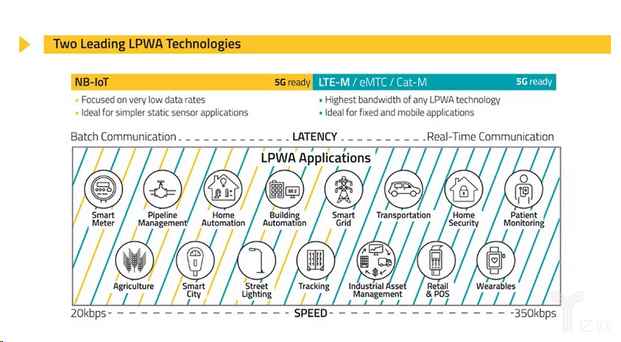
NB-IoT and LTE-M are the internets of Things from 4G to 5G cellular networks.
Both NB-IoT and LTE-M are two LPWAN technologies developed for IoT applications. They are both protocols for low-bandwidth cellular communication. They are designed for IoT devices that need to transmit a small amount of data. They have lower costs and long battery life.
It is worth noting that both NB-IoT and LTE-M are 4G technologies. The initial design of NB-IoT and LTE-M ensured that they can operate in-band in the LTE system and can share the LTE spectrum, as well as for 5G NR.
In the future, NB-IoT and LTE-M will be able to perform in-band operation or coexistence in 5G. This provides forward compatibility with 5G for NB-IoT and LTE-M.
The demand for the Internet of Things on the network
The emergence of NB-IoT and LTE-M is not accidental, and there are other solutions for the Internet of Things before this. The rise of LPWAN is mainly due to the popularity of the Internet of Things, but traditional cellular network solutions like LTE usually consume too much power.
In addition, they are not suitable for applications where data is transmitted infrequently and with a small amount of data. For example, a meter that reads water level, gas consumption, or electricity usage.
The Internet of Things needs a solution that can provide low power consumption and wide coverage.
Generally, the following four points need to be met:
- Low technical cost, supports wider deployment, and improves the return on investment of applications.
- Low power consumption, battery life needs to be very long.
- It covers a wide range and can be connected to equipment underground, in buildings, and in rural environments.
- With high connection capacity, a large number of IoT devices will be connected to the IoT in the future, which will undoubtedly be a huge load.
What is Cat-1?
Cat-1 represents an early push to use existing LTE networks to connect IoT devices. Although the performance is not as good as the 3G network, it is an excellent choice for IoT applications that require a browser interface or voice function. The important thing is that it has been standardized and the Internet of Things is easily transitioned to the Cat-1 network.
What is Cat-0?
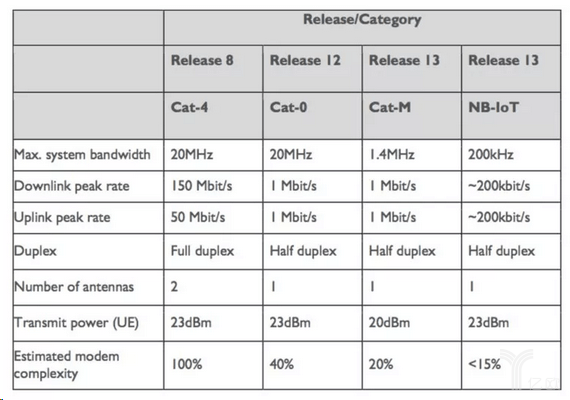
After Cat-1, there was Cat-0. Compared with Cat-1, it optimizes the cost, eliminates the high data requirements supported by Cat-1, abandons support for MIMO, simplifies to half-duplex, reduces the peak rate to 1Mbit/s, and reduces the terminal complexity to 40% of ordinary LTE terminals.
How about LTE Cat-M1, Cat-M and LTE-M?
LTE-M is generally regarded as a second-generation LTE chip built for IoT applications. He completed the low cost and low power consumption originally envisioned by Cat-0. By limiting the maximum system bandwidth to 1.4MHz instead of Cat-0’s 20MHz.
The real advantage of Cat-M over other solutions is that Cat-M is compatible with existing LTE networks. For operators, this is good news, because they don’t need to spend money to build new antennas, even though Cat-M needs a software patch to connect to the LTE network.
How about NB-IoT and Cat-M2?
The purpose of NB-IoT is similar to Cat-M, but it uses DSSS modulation instead of LTE radio. Therefore, NB-IoT does not operate in the LTE frequency band, which means that the cost for suppliers to deploy NB-IoT in the early stage will be higher.
Nevertheless, NB-IoT is touted as a potentially cheaper option because it eliminates the need for gateways. The infrastructure of other schemes usually has a gateway that aggregates sensor data, and then the gateway communicates with the main server. However, with NB-IoT, the sensor data will be sent directly to the main server.
The pros and cons of NB-IoT and LTE-M
Both LTE-M and NB-IoT belong to the category of M2M communication, also known as MTC (Machine Type Communication). And both are specially designed and optimized for IoT devices that transmit a small amount of data for a long time. Both have specific application scenarios.
LTE-M
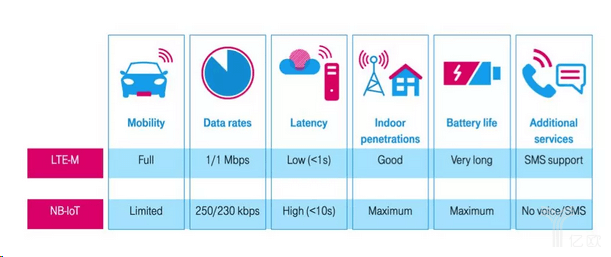
LTE-M has lower equipment complexity, supports large-scale connection density, low equipment power consumption, low latency, and provides wide coverage while allowing services to reuse LTE infrastructure.
For mission-critical applications, LTE-M is the only option. It supports devices that require real-time communication to ensure that applications meet user experience requirements. LTE-M supports voice, and LTE-M uplink and downlink speeds are up to 1 Mbps, far exceeding NB-IoT.
Although LTE-M technology supports voice, each network operator has to decide whether to support voice in LTE-M technology. Secondly, in the case of extended coverage, voice cannot be used for LTE-M at all, and voice is only supported in the standard coverage area.
NB-IoT
NB-IoT is a solution to achieve efficient communication and long battery life of large-scale distributed devices, using mobile Internet to connect these things. NB-IoT is characterized by improved indoor coverage (with stronger penetration), support for a large number of low-throughput devices, low latency sensitivity, ultra-low device costs, low device power consumption, and optimized network architecture.
In the field of healthcare, many patient monitoring devices only need to record and transmit a small amount of data on the patient’s condition to the hospital.
In agriculture, the amount of weather or soil condition data that needs to be transmitted is very small, and for smart cities, sensors to detect the fullness of urban trash bins or the degree of air pollution do not require high amounts of data. At this time NB-IoT will be a better choice.
The NB-IoT and LTE-M cover a wide range of applications. For real-time monitoring, you may need high bandwidth. For asset tracking, the data throughput is small, but as the object moves, there will inevitably be a lot of switching.
Smart meters and many smart city use cases require small data transfers once or twice a day. This means that no single technology can meet the specific needs of IoT devices.
Internet of Things on the road
3G UMTS and 4G LTE technologies use different core networks, which will generate additional complexity and cost. Operators also need to abandon 3G technology to enter single-core networks. The same problem does not appear in the 5G core network, which can be connected to 5G NR and 5G LTE.
In order to ensure similar compatibility between LTE-M and NB-IoT, 3GPP is studying a mechanism that allows NB-IoT and LTE-M to connect to the 5G core network. This will enable future 5G systems to use the same core network to support LTE, NR, NB-IoT, and LTE-M.
NB-IoT and LTE-M have just started. In the next few years, these low-power cellular networks will open the door to a large number of new applications, connecting billions of devices that require remote connectivity and extended battery life.
If you have any NB-IoT and LTE-M antenna questions, please read our ANTENNA FAQ section, if you still cannot get the answer you need, please contact us.
You may also be interested in the below articles.




