WLAN definition
WLAN is the abbreviation of Wireless Local Area Network, which refers to the application of wireless communication technology to interconnect computer equipment to form a network system that can communicate with each other and realize resource sharing.
A Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN) wireless LAN is a wireless computer network that links two or more devices using wireless communication to form a local area network within a limited area such as a home, school, computer laboratory, campus, or office building.
The essential feature of a wireless local area network (WLAN) is that it no longer uses a communication cable to connect the computer to the network, but connects it wirelessly, which makes the construction of the network and the movement of the terminal more flexible.
It is a very convenient data transmission system. It uses radiofrequency (RF) technology and uses electromagnetic waves to replace the old-style twisted-pair copper wire (Coaxial) in the local area network. It communicates in the air and makes a wireless local area network. It can be easily used.
WLAN started in 1997. In June of that year, the first wireless LAN standard IEEE802.11 was formally promulgated and implemented, providing a unified standard for wireless LAN technology, but the transmission rate at that time was only 1~2 Mbit/s.
Subsequently, the IEEE committee began to formulate new WLAN standards, which were named IEEE802.11a and IEEE802.11b. The IEEE802. LLB standard was first formally promulgated in September 1999, and its rate is 11 Mbit/s.
The improved IEEE 802.11a standard was officially promulgated at the end of 2001, and its transmission rate can reach 54 Mbit/s, which is almost 5 times that of the IEEE 802.11b standard. Nevertheless, the application of WLAN has not really started because the entire WLAN application environment is immature.
After more than two years of development, wireless network products and applications are based on IEEE 802. LLB standards have been quite mature, but after all, the access rate of 11 Mbit/s is far from being able to meet the application requirements of actual networks.
WLAN Pros and cons
WLAN advantage
Flexibility and mobility
In a wired network, the placement of network equipment is restricted by the location of the network, while a wireless local area network can be connected to the network at any location within the wireless signal coverage area.
Another biggest advantage of wireless local area network is its mobility. Users connected to the wireless local area network can move and stay connected to the network at the same time.
Easy to install
A wireless local area network can eliminate or minimize the workload of network wiring. Generally, as long as one or more access point devices are installed, a local area network covering the entire area can be established.
Easy to carry out network planning and adjustment
For wired networks, changes in office locations or network topology usually mean rebuilding the network. Rewiring is an expensive, time-consuming, wasteful and trivial process. Wireless LAN can avoid or reduce the occurrence of the above situations.
Easy to locate the fault
Once a physical failure occurs in a wired network, especially a network interruption caused by a poor line connection, it is often difficult to find out, and a high price is required to repair the line.
The wireless network is easy to locate the fault, and the network connection can be restored by replacing the faulty device.
Easy to expand
There are a variety of configuration methods for wireless local area networks, which can quickly expand from a small local area network with only a few users to a large network with thousands of users and can provide features that cannot be achieved by wired networks such as roaming between nodes.
Because of the many advantages of wireless local area networks, its development is very rapid. Now, wireless local area networks have been widely used in enterprises, hospitals, shops, factories, and schools.
WLAN insufficient
While wireless local area networks can bring convenience and practicality to network users, they also have some shortcomings. The shortcomings of wireless local area network are reflected in the following aspects.
Performance
Wireless local area networks rely on radio waves for transmission. These waves are transmitted through wireless transmitters, and buildings, vehicles, trees, and other obstacles may hinder the transmission of electromagnetic waves, which will affect the performance of the network.
Speed
The transmission rate of the wireless channel is much lower than that of the wired channel. The maximum transmission rate of wireless local area network is 1Gbit/s, which is only suitable for personal terminals and small-scale network applications.
Security
In essence, radio waves do not require the establishment of a physical connection channel, and wireless signals are divergent. In theory, it is easy to monitor any signal within the radio wave broadcast range, causing communication information to leak.
WLAN topology
The wireless local area network based on the IEEE802.11 standard allows the use of the 2.4GHz or 5GHz radio frequency band in the ISM frequency band that does not need to be authorized for wireless connection in the local area network environment. They are widely used, from homes to businesses to Internet access hotspots.
Simple home wireless WLAN
In the most common and cheapest example of home wireless LAN, a device acts as a firewall, router, switch, and wireless access point.
Usually, the basic module provides Wi-Fi for 2.4GHz 802.11b/g operation, while the higher-end module will provide dual-band Wi-Fi or high-speed MIMO performance.
Wireless bridging
When wired to Ethernet or need to establish a second redundant connection for the wired connection as a backup, wireless bridging allows wireless connections between buildings.
802.11 devices are usually used for this application, as well as wireless fiber optic bridges. Basic 802.11 solutions are generally cheaper and do not require direct visibility between antennas, but are much slower than fiber optic solutions.
802.11 solutions typically operate in the range of 5 to 30mbps, while fiber optic solutions operate in the range of 100 to 1000mbps.
Medium WLAN
Medium-sized companies traditionally use a simple design, they simply provide multiple access points to all facilities that require wireless coverage. This particular method is probably the most versatile because of its low entry cost, although it becomes difficult to manage once the number of access points exceeds a certain limit.
Large WLAN
Switching wireless local area networks is the latest development in wireless networking, and simplified access points are controlled by several centralized wireless controllers.
Another benefit of switching wireless LANs is low-latency roaming. This allows delay-sensitive applications such as VoIP and Citrix. The switching time will occur within approximately 50 milliseconds, which is usually not obvious.
Requirements for setting up a wireless network
Since wireless local area networks need to support high-speed and burst data services, it is also necessary to solve problems such as multipath fading and crosstalk between subnets for indoor use. Specifically, the wireless local area network must meet the following technical requirements.
Reliability
The packet loss rate of the wireless LAN system should be lower than 10-5, and the bit error rate should be lower than 10-8.
Compatibility
For indoor wireless LAN, it should be as compatible as possible with the existing wired LAN in the network operating system and network software.
Data rate
In order to meet the needs of LAN traffic, the data transmission rate of wireless LAN should be above 54Mbps.
Communication confidentiality
As data is transmitted in the air through wireless media, wireless local area networks must take effective measures at different levels to improve communication confidentiality and data security.
Mobility
Support full mobile network or semi-mobile network.
Energy-saving management
When there is no data transmission and reception, the site machine is put in a dormant state and then activated when there is data transmission and reception, so as to achieve the purpose of saving power consumption.
Miniaturization and low price
This is the key to the popularization of wireless local area networks.
Electromagnetic environment
The wireless local area network should consider the influence of electromagnetic on the human body and the surrounding environment.
When setting up a wireless local area network, it is often necessary to carefully consider many detailed factors to successfully build a wireless local area network and ensure its high working performance.
When connecting to a remote LAN through a wireless LAN, the building where the remote LAN is located should be as visible as possible. If the wireless LAN needs to pass through obstacles such as tall buildings or dense trees, the transmission performance of the built wireless LAN will be affected. Impact, after all, those obstacles will directly affect the normal transmission of wireless LAN data signals.
When the distance between the remote network and the local area network is relatively long, the network transmission bandwidth can be appropriately reduced to achieve the purpose of long-distance data transmission.
If you really need to carry out long-distance wireless transmission, you might as well try to set up a wireless LAN relay transfer station in the middle, so that the Internet signal can bypass obstacles.
In a wireless local area network, when network signals are transmitted over short distances, in order to ensure that the maximum transmission bandwidth can be obtained, several wireless network bridges must be integrated with each other, and the antenna height of the wireless local area network is basically not affected.
It is also very important to properly set the antenna height of the wireless local area network. If the antenna height of the wireless local area network device is not set appropriately, simply relying on methods such as increasing the antenna gain or increasing the power amplification will result in very limited wireless transmission effects.
Then you can consider arranging the antenna of the wireless node device on the top floor of the building and try to use a small antenna to ensure the relative concentration of radio waves, which is beneficial to effectively avoid interference from other wireless LAN signals.
Although frequency hopping technology is used for wireless LAN transmission, the frequency carrier of the Internet signal is difficult to be detected. Therefore, only when both parties wirelessly set the same network ID number, can the wireless Internet signal be safely transmitted.
If you want to further ensure the operational safety of the wireless local area network, you can also encrypt the wireless Internet signal.
Networking mode
Combining several devices in the WLAN can form a multi-level, wireless, and wired computer network. Generally speaking, there are two networking modes for wireless local area networks, one is a WLAN without a fixed base station, and the other is a WLAN with a fixed base station.
A WLAN without a fixed base station is a self-contained network, which is mainly suitable for a peer-to-peer network formed between computers with wireless network cards.
A WLAN with a fixed base station is similar to the mechanism of mobile communication. The computer with a wireless network card is connected to the network through a base station (wireless AP or wireless router).
This kind of network is widely used and is usually used to extend the coverage of a wired LAN or as a broadband access method of wireless Internet.
WLAN without a fixed base station
A WLAN without a fixed base station is also called a wireless peer-to-peer network and is the simplest type of wireless local area network structure. The WLAN structure without a fixed base station is a centerless topology.
The communication relationship between the devices connected through the network is equal, but it is only suitable for a small number of computer wireless connection methods (usually 5 hosts, or within the device).
This networking mode does not require fixed facilities, it can be achieved only by installing a wireless network card in each computer, so it is very suitable for the formation of some temporary networks.
WLAN with fixed base station
When the number of computer users in the network reaches a certain number, or when a stable wireless network platform needs to be established, the AP-centric networking mode is generally adopted.
The AP-centric networking mode is also the most common networking mode for wireless local area networks. In this mode, an AP is required to act as a central station, and all sites’ access to the network is controlled by the center.
Hardware equipment
Wireless network card
The role of the wireless network card is basically the same as that of the network card in the Ethernet. As the interface of the wireless local area network, it can realize the connection and communication between the clients of the wireless local area network.
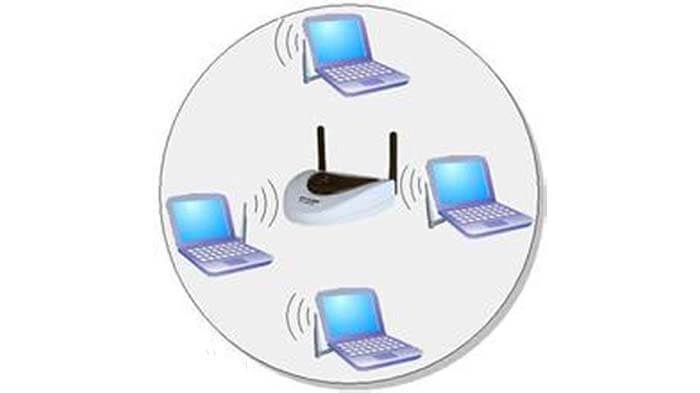
Wireless AP
AP is the abbreviation of Access Point. Wireless AP is the access point and wireless gateway of the wireless local area network. Its function is similar to the hub in the wired network.
Wireless antenna
When the network devices in the wireless network are far apart, as the signal weakens, the transmission rate will drop significantly so that the normal communication of the wireless network cannot be realized. At this time, the received or transmitted signal must be enhanced with the help of the wireless antenna.
User Management
The content of the user management of the wireless local area network includes the emphasis on the management of the files and change records of mobile phone users and the management of the user data of the exchange in the mobile communication;
User management in broadband ADSL networks emphasizes user authentication management and billing management, and of course, also includes user information management;
The distributed system emphasizes the establishment, deletion, permission setting, registration, connection, and accounting of users.
But all user management is nothing more than the main content that usually includes system IP address allocation, user database management, user registration, user level management, user authority settings, user logs, and system working status monitoring.
After introducing a new generation of Internet protocol IPv6, the user management of wireless local area networks mainly deals with the following aspects.
IP address allocation
The wireless local area network from the user to the wireless access point is a wireless link, so there is no IP address allocation problem, but once it enters the access network, the AP that accesses the network will assign a temporary IP to the user.
This IP will be used during the communication between the user and the network until the user leaves the network, the IP is automatically released.
IP address allocation and management in IPv6 networks mainly include passive allocation and active acquisition. The active acquisition is calculated through the relevant protocols of the IPv6 protocol suite and is mainly obtained through the MAC address of the network card using a specific algorithm. Passive allocation is obtained by requesting a DHCPv6 server in the network.
Database
The user database is set up to save the user’s basic personnel information such as name, gender, etc., and its purpose is to force the user to register with the real name, and to check whether the personal information entered during the user registration is correct.
When a user logs on to the website for the first time for user registration, the entire registration process can only be completed when the entered personal information is consistent with the content stored in the database, otherwise, the registration cannot be successful.
This part belongs to the content of application layer management and does not require much change after being combined with IPv6.
Registered
User registration is the basis for the classification and hierarchical management of end users to ensure the orderly operation of the system. User registration information is the basis for the system to determine whether a visiting user is a registered user.
To prevent employees with ulterior motives from registering under false names, the client’s IP address and user name, user password, and other personal information can be bundled for verification.
After being combined with IPv6, the IPv6 protocol itself provides good security, and we can make full use of some of the advantages of IPv6 to make user registration more complete.
Sign in
When the terminal accesses the network, the network can automatically obtain the IP address of the visiting client and compare the IP address with the record in the user registration database to determine whether the visitor is a registered user.
If the client’s IP address-related information is not found in the database, indicating that it is a terminal that has not been registered, it will be guided to register as a user;
If the IP address registration information exists in the user registry, it indicates that the client has already been registered, and the user will be prompted to enter his personal information, name, password, etc., and then compare it with the record in the user registry to verify the user’s password and confirm the user’s identity.
The confirmed user will be automatically given an identity by the system, and the user’s identity information whose life cannot be obtained and changed on the terminal can be controlled by the system.
Level setting
Users usually have a clear and fixed job position in units and organizations, belonging to a certain department and group, and located at a certain administrative level. Different levels of users are set by the system administrator based on personnel information and user registration information.
After this part is combined with IPv6, there is basically no change, that is, there will not be much change in the access WLAN network in the next-generation all-IP network.
Permission settings
In order to prevent users from unauthorized access and arbitrary information publishing activities, user rights must be restricted. Of course, this has nothing to do with the specific network protocol, so there is no change in the next-generation IPv6 network.
Log
The user log is the first-hand data to record the click-through rate of the user activity statistical information column and analyze and improve the network utilization.
The user log is saved in the database, which is convenient for future statistical analysis. The user log information can be used for statistical analysis such as the information published by the site and the column browsed by the user during the login time.
This part belongs to the operation of the application layer. After the introduction of IPv6 technology, no changes are required.
The typical application scenarios of WLAN are as follows.
Between buildings
It is simple and cheap to build a network connection between buildings, instead of dedicated lines.
Catering and retail
The catering service industry can use wireless local area network products, directly from the table to input and transmit the content of the guests’ order to the kitchen and counter. Retailers can use wireless local area network products to set up temporary cashier counters when promoting sales.
Medical treatment
Using portable computers with wireless local area network products to obtain real-time information, medical staff can avoid delays in treating patients, unnecessary paperwork, delays in document circulation, and misdiagnosis, and improve the quality of care for patients.
Enterprise
When employees in the enterprise use wireless local area network products, no matter where they are in any corner of the office, they can send e-mails, share files and browse the Internet at will.
Warehouse management
General warehouse staff can input the latest data into the computer warehouse system immediately through the application of a wireless network.
Container terminal
In general, the bridge crane trucks in the container terminal can transmit real-time information back to the office when the containers are mobilized, so as to facilitate the line-by-line operation of related operations.
Monitoring system
Generally located in a remote place where the site needs to be monitored, due to the difficulty of wiring, the remote image can be transmitted back to the main control station through the wireless network.
Exhibition venue
Such as the general electronic exhibition, or computer exhibition, because the network demand is extremely high, and the wiring will make the venue appear messy, so if you can use a wireless network, it is a better choice.
You may also be interested in the below articles.